Conductors with Anti-Ice treatments offer a significant reduction in ice sleeves, avoiding damage related to extreme climatic events and increasing the resilience of overhead power grids.
The environmental conditions affect the operation of the conductor and, clearly, influence the layout that this must have. Normally, with each design request for a new conductor, in addition to the required requirements (e.g. the ampacity), the customer shares a document with the environmental and overload conditions characteristic of the region in which the conductor will have to be installed. A fundamental parameter of this document is the overload condition due to ice. The accumulation of ice sleeves on the conductors can cause disruptions (e.g. blackout), safety problems as under the weight of the ice the conductor’s arrow increases reducing the distance from the ground and, in some cases, also leading to the conductor rupture.

How to limit the accumulation of ice on conductors?
De Angeli Prodotti has designed and developed a coated Anti-Ice conductor with a paint that contains particular nanoparticles capable of modifying the wettability of the surface making it superhydrophobic, in order to mitigate the development of the ice sleeve on the conductor.
What is the wettability of a surface?
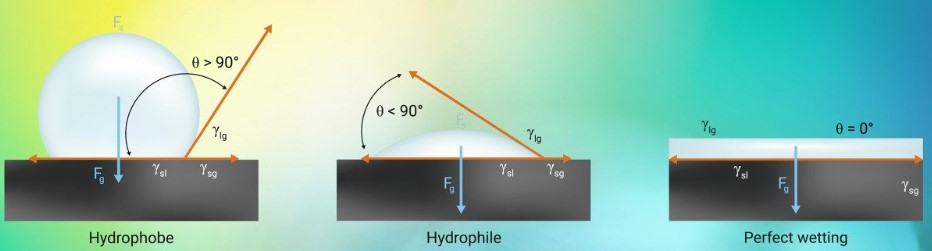
Wettability is the process that brings a liquid and a solid surface into contact. This occurs in the presence of a gas phase or another liquid phase, immiscible with the first, which can be described in general terms as fluids. The system is fully described by the contact angle (θ), defined as the angle formed by the tangent to the liquid-fluid interface, and by the tangent to the solid surface, at the contact line between the three phases.
A low contact angle (θ<90°) describes a situation in which the solid is partially wetted by the liquid (hydrophilicity, in the case of water), while a high contact angle (θ>90°) describes a situation in which the solid is not very wet (hydrophobicity, in the case of water). It is a property that influences the obtaining of both superhydrophobic and superhydrophilic surfaces and is evaluated by contact angle tests. Superhydrophilicity, which literally means “strong affinity with water”, gives the surface maximum wettability, thanks to the contact angle between the drop and the surface of less than 5°, with the formation of a continuous thin film. On the contrary in the presence of superhydrophobicity (“strong fear of water”), for contact angles greater than 150 °, there is no wettability, favouring the formation of isolated drops.
What are the advantages of Anti-Ice conductors?
The Anti-Ice treatments offer a significant reduction and/or elimination of ice sleeves, which can cause the conductors to break, and allow to avoid damage related to extreme climatic events and increase the resilience of overhead power lines.
De Angeli Prodotti is able to apply this surface treatment to any conductor regardless of layout, materials or dimensions.